Web3 feels powerful, but the messy backend work slows every developer down. You juggle scripts, RPC listeners, cron jobs, and quick fixes just to keep your dApp stable. Web3 workflow automation removes this clutter and gives you simple, predictable logic you can rely on. Tools like Kwala push this even further by offering no-code flows designed specifically for decentralized app automation. We’ll walk through how web3 […]
Read MoreMost teams do not notice a smart contract problem right away. They notice it when support tickets pile up or gas costs suddenly look ridiculous. By then, the damage is already done and users have felt the impact.
That is exactly why smart contract health monitoring exists. Kwala smart contract monitoring uses Web3 workflow automation for monitoring to react when contract behavior starts changing, not after things break.
From gas usage anomaly detection Web3 to smart contract error rate detection, this blog explains how the pieces fit together and why Kwala makes monitoring easier.
What is smart contract health monitoring?
Smart contract health monitoring is the practice of continuously observing how a smart contract behaves after deployment, not just whether it exists on-chain.
It focuses on tracking real signals like event frequency, transaction success rates, execution delays, and gas usage patterns to catch problems early.
Here’s how it helps:
- Detects rising failure rates and silent transaction reverts before they affect users
- Flags unusual gas spikes through early gas usage anomaly detection Web3 signals
- Identifies stalled or inactive contracts when expected events stop firing
- Reduces reliance on manual checks and fragile monitoring scripts
- Improves reliability by enabling faster responses to contract issues
Monitoring keeps contracts predictable, even when everything else around them changes.
Why traditional monitoring breaks at scale
Most teams start with simple scripts and RPC listeners to handle smart contract health monitoring. It works early on, especially for single-chain setups. As usage grows, this approach starts to crack and becomes harder to maintain.
Here’s why it breaks down:
- Polling infrastructure makes Web3 workflow automation for monitoring expensive and fragile at scale
- Event listeners require constant maintenance, weakening long-term smart contract error rate detection
- Cross-chain setups multiply complexity and reduce visibility across networks
- Backend servers reintroduce centralization and operational risk
- Debugging gas spikes and failures makes gas usage anomaly detection Web3 slow and reactive
Over time, every dApp turns into a backend-heavy system, where monitoring becomes the biggest operational burden instead of a safeguard.
How Kwala changes the monitoring model
Kwala was built to help teams react to blockchain activity without running heavy infrastructure. Instead of treating blockchains as systems that need constant checking, it treats them as systems that should trigger action only when something meaningful happens.

This approach makes Kwala a natural fit for smart contract health monitoring. It flips monitoring from polling to event-driven workflows. Teams move from “check every block” to “react only when something happens,” using deterministic workflows that respond to real on-chain signals.
What this enables:
- Event-driven triggers for Kwala smart contract monitoring
- Deterministic workflows for Web3 workflow automation for monitoring
- No polling, cron jobs, or long-running listeners
- Faster insight into smart contract error rate detection
- Scalable gas usage anomaly detection Web3
All of this keeps monitoring lightweight and predictable. Teams spend less time maintaining systems and more time responding to real issues.
Step-by-step workflow setup for contract health monitoring in Kwala
Now that the monitoring model is clear, the next step is learning how to set it up in practice. The goal is not to cover every possible edge case on day one, but to build a workflow that catches the most important failures early.
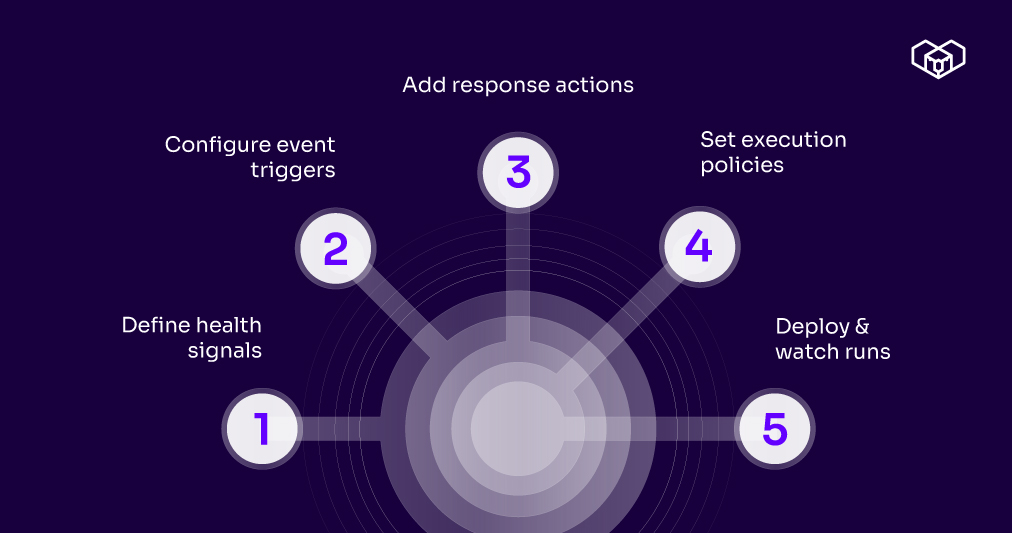
Below is how to approach smart contract health monitoring using a simple, structured setup.
Step 1: Define health signals
Start by deciding what “healthy” looks like for your contract. In the Kwala dashboard, identify signals such as expected event frequency, maximum acceptable execution delay, or known failure events.
Keep this simple at first. Focus on high-impact failures and avoid edge cases until the core workflow is stable.
Step 2: Configure event triggers
Select the contract you want to monitor and choose the event that represents activity or risk. Extract event parameters using built-in event indexing. There is no need for regex or custom parsers, which keeps monitoring deterministic and easier to maintain.
Step 3: Define response actions
Decide what should happen when a health check fails. Kwala allows you to send alerts, trigger webhooks, execute compensating transactions, or log immutable audit records. Automated responses should handle most cases, with manual escalation as a fallback.
Step 4: Set execution policies
Finally, configure execution rules such as retry behavior, expiry, and cross-chain dependencies. These settings prevent alert storms and ensure workflows stop cleanly instead of running endlessly.
Simplifying smart contract health monitoring with Kwala
Smart contracts do not need more scripts or constant checking. They need a monitoring approach that reacts to real behavior and scales as systems grow.
Kwala smart contract monitoring makes smart contract health monitoring easier by replacing polling with event-driven workflows that respond only when something changes.
With Web3 workflow automation for monitoring, teams can catch issues like gas usage anomaly detection Web3 and smart contract error rate detection early, without maintaining backend infrastructure.
Start monitoring your smart contracts with Kwala
FAQs on smart contract health monitoring
What is the concept of a smart contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing program stored on a blockchain that runs when predefined conditions are met. It removes intermediaries and enables automated, trust-based transactions across Web3 systems.
Can ChatGPT write smart contracts?
ChatGPT can help draft, explain, or review smart contract code, but it should not be used as a final source. All generated contracts must be audited and monitored using smart contract health monitoring practices.
How to check if a smart contract is safe?
Smart contract safety is checked through code audits, testing, and ongoing smart contract error rate detection and gas usage anomaly detection Web3. Continuous monitoring helps catch risks after deployment.



 book a call with us
book a call with us 

